A 404 error or 404 page not found is a standard error when making search inquiries with Google Analytics. However, don’t panic, as there are many types of 404 errors. Some are incredibly easy to fix and have no detrimental impact on your SEO or digital content. Yet, some need to be fixed immediately to prevent any harm to your website.
With that in mind, you will learn all you need to know about 404 pages not found errors in this 404 errors ultimate guide. This tutorial includes what a 404 is, why a 404 is terrible for your SEO and content, tools to track 404 issues on your website, resolving 404s using different approaches, and methods to avoid them in the future.
Table of contents
| People also read: SaaS Content Marketing Strategy: 5 Tips to Make It Effective 30 Best Things to Sell for Christmas 2022 Everything You Need to Know About SEO for Small Businesses |
What Is a 404 Error?
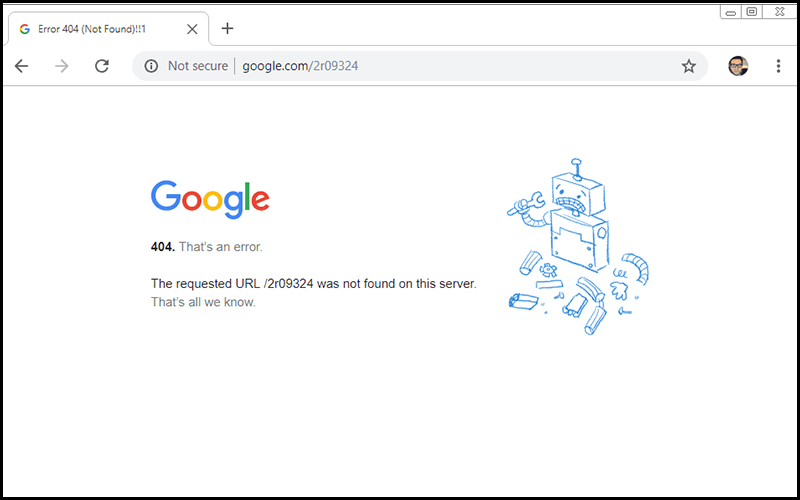
A 404 page is a website landing page that informs users that the requested page is either unavailable or does not exist. Its primary function is to notify users that they’ve arrived at a 404 error page.
404 not found errors are a type of HTTP status code indicating that the page a user is looking for on a website is unavailable on the server. When a page loads in a browser, the HTTP header contains a response status code generally hidden from view. These answers are categorized into five groups:
- 100-199 are informational responses
- 200-299 are successful responses
- 300-399 denote redirects
- 400-499 denote client errors
- 500-599 denote server errors
A 404 not found error (also known as an HTTP 404 or 404 code) is a sort of client error that is highly specific. It implies that the page the viewer is looking for isn’t available on the server.
1. When and Why a 404 Error Occurs
Websites are constantly evolving. Content is moved around, linkages are broken, and pages get renamed. A 404 Page not Found can be caused by any of these factors. This means that despite being able to connect to the server, your browser could not locate the requested site connected to the URL.
404 errors can be caused by a variety of reasons. Here, we split those reasons into two main sections: user-focused and developer-focused errors.
Visitors-focused errors

- Internal 404 Errors – One of your page’s links to another page on your website; however, the link leads to a 404 error page. This can happen if visitors misspell a URL, link to a defunct page, or have a broken outbound link that accidentally links to your website.
- Inbound 404 Errors – occur when a link from elsewhere on the internet points back to your website, resulting in a 404 page. This can happen if someone mistyped the URL or linked to a page that no longer exists.
- Outbound 404 Errors – occur when you connect to someone else’s website and the link redirects to a 404 page because the URL was mistyped or the page is no longer available.
- Images and Embeds 404 Errors – occur when photos or videos do not appear on your page due to an issue, such as the image being deleted or a mistake in the source code used to create the image.
Website-focused errors

- The malware sends users to a 404 error page – What you can do here is check for viruses and spam on your website.
- Memory limits stop a visitor from seeing your page – To fix this, make sure your PHP memory and server resource limitations aren’t exceeded.
- Problems with your .htaccess file – You should run your .htaccess file to confirm that it is not causing 404 errors by accident.
- SSL certificate issues – An audit should be conducted to ensure that adding or changing SSL did not result in 404s.
- Too many redirects – When in use, bots frequently wind up at a 404 page after roughly 5 redirections. Consider examining the redirection path to see if any shortcuts can be made.
- Unresponsive servers normally provide a different error. However, they can also generate 404 errors – Here, the server’s error logs should be examined.
2. Soft 404 vs. Hard 404

While you’ll almost certainly stumble upon a complex 404 request while exploring a website, you’re unlikely to encounter a soft 404 problem unless Google Search Console alerts you.
When a non-existent page on your site displays a “not found” notice to visitors yet gives a 200 OK status to search engines, this is known as a soft 404. This informs Google and other search engines that the URL contains a page. Crawlers lose time trying to crawl and rank the URL as a result.
The problem is that Google is quite excellent at detecting these false pages.
It slaps a soft 404 error on a website receiving a 200 OK status with all the attributes of a page that should return a 404 code and alerts the site owner in Google Search Console when it discovers a messenger bearing a 200 OK status with all the properties of a page that should return a 404 code.
How Can 404 Errors Affect Your Website’s SEO?
Whether or not a 404 error hurts your SEO depends heavily on the nature of the error itself.

Let’s begin from the user’s perspective. When users keep getting 404 errors while exploring your site, it will be a bad experience. A single 404 error might be enough to drive a visitor away.
Even worse, 404 errors might harm your search engine results.
The more broken links you have on your site, the more difficult it is for Google and other search engines to scan them. The succession rate of your site’s link equity being transferred around won’t be high.
You may have significant bounce rates if people abandon your site after arriving at a 404 page. Bounce rates, unlike 404 errors, are a ranking factor, and Google may punish you.
Many SEO professionals have observed a link between 404 error correction and enhanced crawling and ranking. In other words, Google favors websites that clean up their acts. Obviously, it’s not a cause-and-effect relationship, but it’s one that’s been well-documented.
Don’t be alarmed if you get 404 errors. While 404 errors might seem complicated, they aren’t as problematic as they appear. It’s in your best interests to resolve 404 problems as soon as possible to better serve visitors and indirectly influence your rankings.
How to Detect and Fix 404 Errors on Your Website
There are various choices regarding finding and exposing 404 errors, each with varying degrees of effort and depth. Because it’s something you’re already familiar with and understand well, looking at your website for 404 errors is the simplest way to learn about them. So, let’s start with a selection of tools to find 404 errors on your website.
1. 404 Errors Detecting Tools
- MonsterInsights (formerly known as Yoast Analytics) adds additional tracking to your Google Analytics reports, making detecting 404s a breeze. As soon as you link your Google Analytics account, it starts tracking your 404 failures.
- Site crawlers like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, and SEMrush are also good ways to detect 404 errors. Simply conduct a site audit, then click on Response Codes in the top menu to identify 404s using Screaming Frog. Screaming Frog will show every website with a 404 status code if you filter for Client Error (4XX).
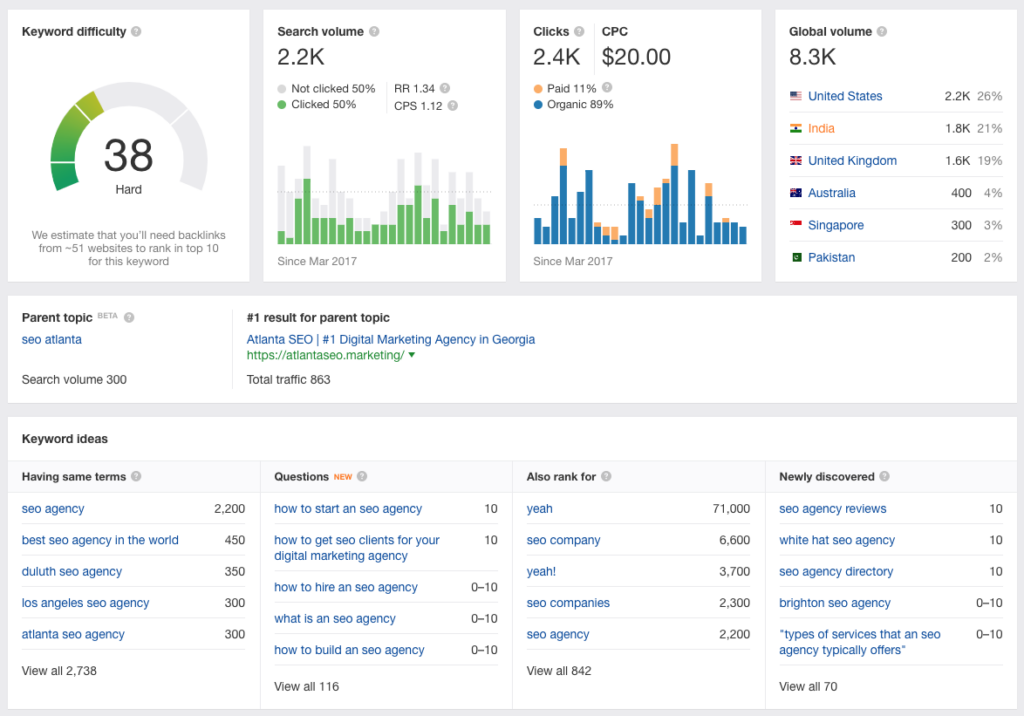
- Google Search Console is another valuable tool for locating 404 problems on your website. To view the 404 issues that Google Bots discovered on your site, all you have to do is… Log in to Search Console, click Coverage, then the Excluded tab. There’s a list of problematic 404 errors labeled Not Found (404) and soft 404 errors labeled Soft 404 on that page.
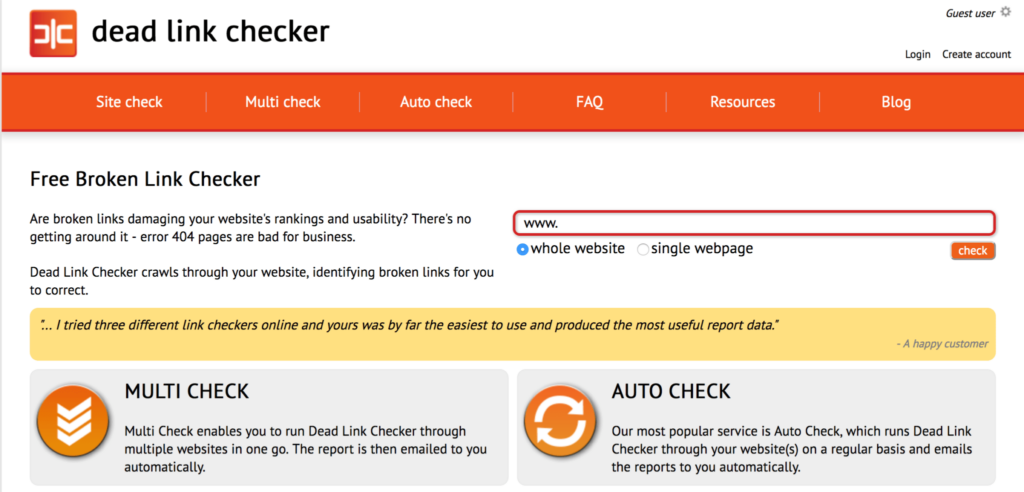
- Similar to Screaming Frog, Dead Link Checker is a scanning tool that can scan up to 2000 links on your website for broken links. Within a few minutes, it searches your page or the entire site and generates a broken links report. The report is created without installing or running any extra application files. The Broken Link Checker then shows which links are working and which are not.
2. How Often Should You Check for 404 errors?
Frequently checking your website for 404 errors is a relatively safe practice. How frequent, you may ask? Smaller sites with fewer than 50 pages should generally check for 404 problems once or twice a month. Larger sites may wish to check for 404 problems weekly or biweekly. Major websites with a sizable content network should increase the frequency and check daily or bidaily. Being cautious of these errors by detecting them ahead of time will help you save time and effort.
How to Fix 404 Errors
Now that you’ve discovered your website’s 404 problems, it’s time to figure out how to correct them. The problem with 404 errors is that locating them isn’t nearly as essential as determining what to do about them. There are four main ways to fix a “404 not found” error:
- Redirect the 404 error: The simplest approach to repair 404 problems on your site is to use a 301 redirect to send readers to another relevant page. When using 301 redirects, be sure to send the link to an appropriate page – sending the link to an unsuitable destination might hurt your ranking performance.
- Restore the page: Consider reinstating the original form of a page you’ve removed if you discover there’s still a high demand for it and there’s no acceptable page to redirect people to. You can restore the page from an older backup or rebuild it using the Way Back When archives.
- Correct the link: If your site has broken links between pages, just change the source code to redirect to the proper URL. On the other hand, if the broken link is on a third-party domain, send an email to the site owner. If you’re having trouble finding the perfect email address, go no further than our email address guide.
- Make a 404 error page: You may ensure every visit counts by designing a personalized 404 error page.
Furthermore, if the material already exists on your site, a 301 redirect will route users to the correct location. You can accomplish this by changing your .htaccess file and diverting traffic from bad URLs to good ones or using a plugin to handle it.
This type of 404 error occurs when:
- Your link is mistyped.
- You mistype your link.
- You or someone else posted the wrong link.
So, if one of these happens, you may need a 301 direct. 301 redirects carry over whatever SEO value a link provides to the page, allowing you to keep any SEO work you’ve done, even if the link was wrong.
When possible, update the erroneous link and do a 301 redirect, as determining the cause of 404 errors is crucial to resolving them. You should always try to fix a broken link on your own website.
Also, if you have a lot of 404 errors, prioritize the ones that pertain to turning users into customers above the more informational ones. Generally speaking, product pages should be the main priority, rather than blog articles. 404 problems on product sites, contact pages, and service pages should be addressed first.
Other pages might not be as urgent. Google Search Console might reveal 404 problems on pages that a human user would never be able to find. You’ll want to address these later, but they shouldn’t significantly influence your rankings.
Fixing 404 Errors on WordPress

If you have a WordPress site, you may detect 404 errors by following the same steps above.
After locating them, let’s look at how WordPress 404 not found errors can be resolved.
It’s most likely a problem with your permalinks if you’re getting site-wide issues. To adjust your permalinks settings, go to Settings → Permalinks.

When you’ve finished, go to the bottom of the page and click Save Changes.
You’ll want to put up a 301 redirect for any pages returning 404 errors. WordPress will attempt to accomplish this automatically, but it may fail.
Getting Yoast Premium or installing the Redirection plugin is the simplest method to accomplish it yourself.
Go to Tools → Redirection after it’s been installed and activated.
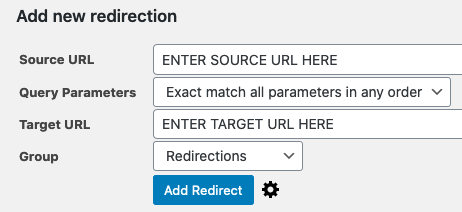
You’ll need to answer a few simple questions to use the tool.
Then, on your WordPress site, you’ll be able to redirect any URL. Simply put, type the URL you want to turn the page to in the Source URL box and type the URL you want to redirect the page to in the Target URL field.
Then select Add Redirect from the drop-down menu.
If this process sounds complex or challenging, it’s probably better to get the aid of a website developer or your website hosting support staff to ensure that any 404s are correctly routed.
After that, it’s time to communicate with Google once you’ve corrected all of the 404 problems on your website, set 301 redirects, and fixed any broken links or content. Here’s what to do after you fix the problem:
- After fixing the problems, resubmit your sitemap for Google to validate.
- For broken links, you took action on mark 404 problems as fixed in Search Console. Leave it unresolved if you let it expire on its own.
- Keep an eye on your crawl data and index status in Search Console to observe how dealing with 404s has affected your website. Keep an eye on your impressions in search analytics data as well.
- Make efforts to prevent them from happening again as much as possible because you don’t want to go through this again
How to Create the Best 404 Pages
404 Page Not Found is a common occurrence on the internet. They will occur even if you try your hardest to avoid 404 pages.
As a result, it’s important to be prepared with a fantastic 404 page that guides visitors to where they need to go. When users arrive at 404 pages, they frequently abandon websites because they did not find what they were looking for and are disappointed or perplexed. This isn’t good for SEO.
The default 404 Not Found page design looks like this:
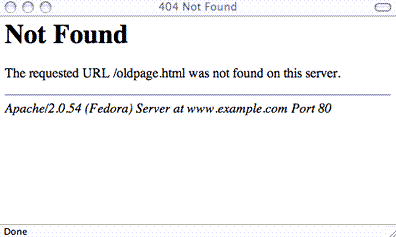
This page design usually frustrates users and provides a poor user experience. Bounce rates might increase due to 404s, which can hurt your SEO. When it comes to 404 errors, using a creative 404 not found page design can be really beneficial.
1. How an Appealing 404 Page Benefits Your Website
It takes time, work, and energy to set up a custom 404 page. But your website can receive massive upsides such as:
- Ensuring that your pages that are difficult to index are crawled.
- Boosting your brand and lowering your bounce rate.
- Engagement of your audience (And Surprise)
- Directing visitors along the right path (to Purchase)
2. The Best Examples for 404 Error Page Design
Below is a list of comprehensive elements that go into a good 404 page on the internet and examples. Try utilizing these factors when building or creating your own 404 pages.
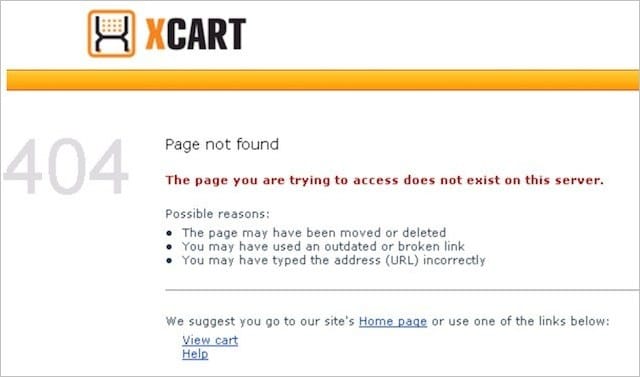
- A good 404 page should use a really simple message that will get the job done. This example from Xcart uses “might” and “may” to avoid blaming customers since 404 errors can result from a user error (mistyped URL)
- Excellent 404-page designs should have a consistent look and feel. Your brand logo, website color scheme, and standard fonts and style should be included in the 404-page design, so customers immediately know they are on your website.
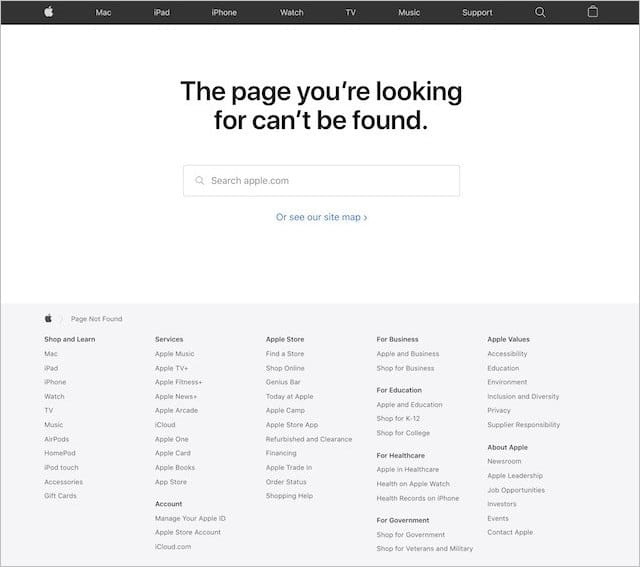
- A 404 page can also direct viewers to your main page. This is a simple technique used a lot by major websites. All you have to do now is add a conspicuous link or button with a clear call to action.
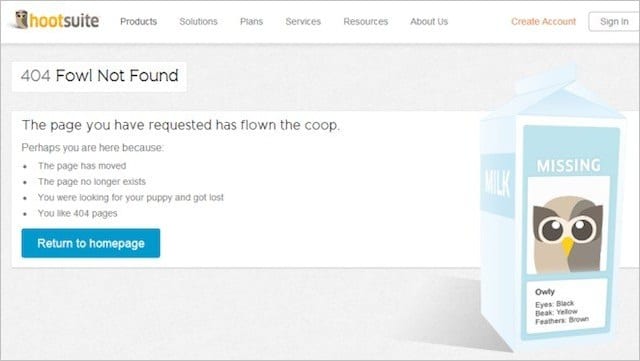
- Your 404 website’s header and footer navigation should be consistent, as well as the 404 page – This ensures that people can browse your website’s key pages quickly and simply.
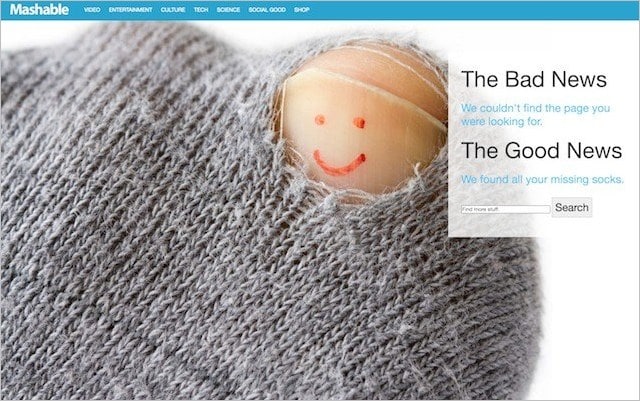
- Your website may incorporate a sense of humor – Landing on a page that says “page not found” might rapidly irritate visitors. A good dose of humor is one of the finest methods to relieve frustration and brighten their mood. A clever joke or engrossing animation may rapidly transform “oh crap” into “that’s awesome”
Wrapping Up
404 Page not Found errors are unavoidable for every website. However, don’t allow them to degrade your site’s user experience or harm your rankings. Use the methods and tools listed above to conduct frequent checks for 404 problems and swiftly resolve them. The less harm they can cause, the faster you can fix them.
Try FREE Magento Page Builder demo today
Looking for a Magento 2 page builder that helps you create any beautiful page layout with no coding required?
Magezon Page Builder can help!
 Magezon Blog Help Merchants Build Comprehensive eCommerce Websites
Magezon Blog Help Merchants Build Comprehensive eCommerce Websites