You are most likely aware of what a transactional email is. They’re most likely inundating your email! Look for emails that validate your accounts, confirm your purchases, or change your password. That is a transactional email.
While you may be acquainted with these emails, you may be curious about how transactional emails function. And, as a developer, manager, or agency, do I need to send transactional emails as well?
Transactional emails may be a practical approach for automatically delivering emails to consumers, depending on their actions and habits. In this post, we’ll define transactional email, look at the best transactional email instances, and explore some tremendous transactional email examples.
Table of contents
- What Is a Transactional Email?
- Know the Difference Between Transactional Emails vs. Marketing Emails
- What Is a Transactional Email Used for?
- Types of Transactional Emails and Best Transactional Email Examples
- Best Practices for Transactional Emails You Should Follow
- Transactional Email Terms Explained
- Wrapping Up
What Is a Transactional Email?

A transactional email is a message delivered automatically to subscribers in response to their activities on a specific application or website. Transactional emails include order confirmations, booking confirmations, subscription confirmations, and notifications.
Transactional emails are communications companies must send to complete a transaction or deliver a requested product or service. As a result, businesses do not require the customer’s approval to send transactional emails.
These emails include order updates, booking confirmations, subscription confirmations, and account-related alerts. For example, when users make an online purchase, they will get an email confirming receipt of their order using a transactional mail program embedded into the application.
A transactional email’s objective is to reassure the client that their action was successful. Failure to send transactional emails can leave your customers perplexed, requiring them to contact support to resolve any issues caused by the absence of communication.
Customers anticipate receiving these emails and will open them faster than other types of communications. Indeed, transactional emails get eight times the number of opens and clicks as different types of emails and can produce six times the money.
As a result, your company must plan to maximize transactional emails’ potential.

Try FREE Email Builder demo today
Looking for a Magento 2 email editor that helps you create Magento transactional emails with no coding required?
Magento 2 Email Builder can help!
Know the Difference Between Transactional Emails vs. Marketing Emails

The fundamental difference between transactional emails and marketing emails is the purpose. Whereas marketing emails are advertising, transactional emails exchange information or provide instructions on proceeding with a transaction (such as account verification emails). Therefore, transactional emails include mostly informative and functional material.
Another distinction between transactional and marketing email is that marketing emails are often sent in bulk at the sender’s discretion. Transactional emails are announcements delivered individually to a person when they engage with your website, landing page, or application (and the message will be triggered themselves).
As a result, individuals do not need to opt in to receive transactional emails. If a consumer purchases anything from your business, you are permitted to send an automatic email confirmation of the transaction. Permission is required to send marketing campaigns. And once you do, you must include an unsubscribe link in each email to allow recipients to opt out.
What Is a Transactional Email Used for?
A Transactional email serves a variety of purposes. The following are the eight most common applications of transactional email.
1. Notifications and Receipt

A transactional email is frequently used to provide eCommerce or retail receipts or information about transactional orders. Additionally, businesses can use those emails to inform clients about their successful checkout and their orders’ delivery. And as direct-to-consumer (D2C) and direct mail continue to rise in popularity, the necessity to appropriately notify customers of their purchase progress becomes even more critical.
2. Alerts About Your Account
“Alerts about your account” notifications are generated in response to customer account changes. Account-related announcements include dunning emails that remind clients of past-due bills or missed payment efforts. These transactional emails inform consumers about billing difficulties and contribute to churn reduction. Without them, clients may be unaware that payment processing issues exist. In addition, dunning emails gently remind clients to amend their billing details if their accounts are nearing deactivation.
Additional account-related alerts also included changes to email addresses and passwords, warnings of failed login attempts, trial expiry reminders, and other account-related difficulties.
3. Requests Made Explicitly
People use this transactional email to provide information consumers of an application or service have requested. The demands are often urgent, meaning people anticipate receiving these emails quickly. A password reset is a classic example of an explicit request. Because users cannot access their accounts without a password, they look forward to a rapid answer when requesting a password reset.
Another instance of explicit request is the verification code used in two-factor authorization, which requires users to provide a temporary password and their regular password to access their accounts. As with password resets, people expect to receive verification codes immediately. Recovering lost product keys and any situation where users cannot access or activate their accounts due to a lack of account-related information also comes into this category.
4. Invitations and Referrals

This email calls out friends and colleagues to sign up for an account by sending referral and invitation emails. Instead of sending an invitation using their email application, customers may input their friends’ email addresses into a form, and the service would send the inviting emails on their behalf. Referral emails function similarly to invitation emails, but the distinction is that referrals are often motivated with a bonus for the sender and, in some instances, the receiver. Gift cards and account credits are examples of rewards.
5. Behavioral Triggers
Behavioral emails are sent to users when they reach particular milestones or circumstances in a service or application. An onboarding email is an example of a behavioral email. After creating accounts, users get welcome emails to assist them in discovering the website/application. Next, a follow-up email might educate them on new features or ensure they’re delighted with the service. Then a third email, and so forth.
Some of the instances of behavioral emails include abandoned carts and reactivation emails. For example, customers who have completed their purchases but have not yet checked out might be sent an automatic email reminding them of incomplete orders. Abandoned cart emails might be sent hours or days later, with special incentives for consumers to finish their purchases. Reactivation emails do the same. When users haven’t logged in for a while or have signed up for a service but never used it, they may get emails encouraging them to do so.
6. Notifications and Updates

The purpose of notifications and updates emails is to notify customers of changes to their policy, billing information, or other transactional facts. This transactional email is often sent to big groups of clients, such as all of a magazine’s subscribers or university students.
7. Notifications Based on Events
Event-driven notifications notify users of various actions, such as event reminders, comment notifications, and shipment updates. Unlike account-related notifications, event-driven notifications generally incorporate activities other individuals make, such as social media or the service itself, like reminders or status changes. For example, users may get event-driven alerts when they receive a new message or are tagged in a social network post. Additionally, they can notify consumers when a shipment has been delivered or when they have an upcoming meeting.
8. Requests for Assistance and Feedback

Customer satisfaction depends on effective service. For instance, it might be infuriating for a consumer to submit a support request but not confirm that it was received. Moreover, if a support staff does not receive a request immediately, the response time may be delayed, frustrating both the consumer and the support team. Support-based transactional emails benefit both parties by facilitating contact and informing everyone of status changes. As with support requests, comments may assist in maintaining a great customer experience. Likewise to how onboarding emails are sent, feedback requests may be sent to consumers after they’ve completed a purchase or registered for an account. If companies get unfavorable feedback, they may contact clients and try to transform unpleasant experiences into good ones.

Try FREE Email Builder demo today
Looking for a Magento 2 email editor that helps you create Magento transactional emails with no coding required?
Magento 2 Email Builder can help!
Types of Transactional Emails and Best Transactional Email Examples
1. Email of Welcome
Welcome emails are exactly what they sound like. They warmly welcome everybody who has recently purchased from you or subscribed to your service.
According to Invesp’s research, welcome emails have an average open rate of 50%, making them 86% more successful than regular newsletters. Additionally, consumers who get a welcome email have a 33% higher level of involvement with the company than those who do not.
Welcome emails have their rhythm — you may express gratitude for the user’s registration and inform them of what they can anticipate from you in the following days.
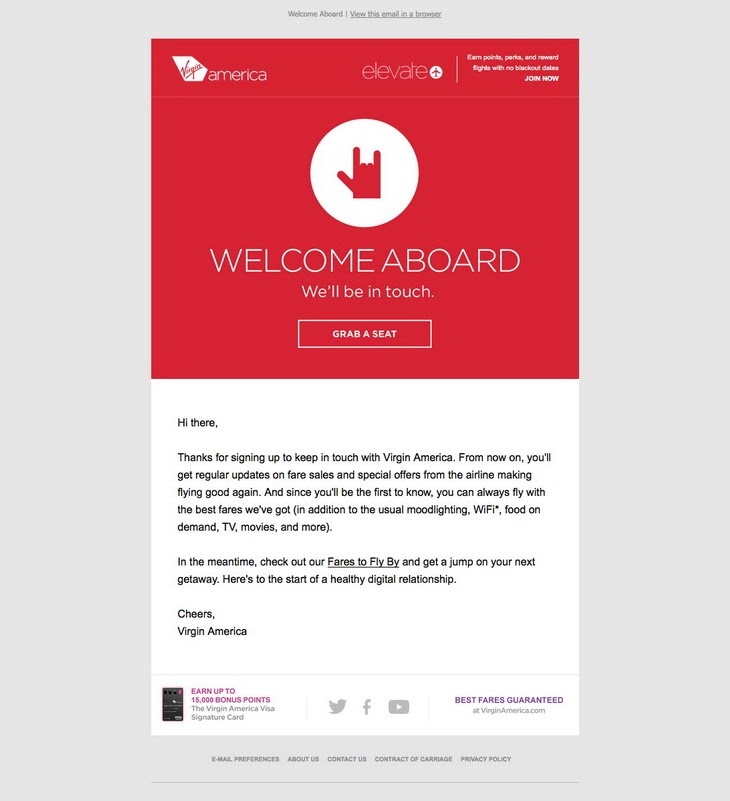
Below is an excellent transactional email example of a Welcome email from Virgin America airlines. They thanked the customer, told them what to expect, and promoted their service.
2. Email Confirmation of Order
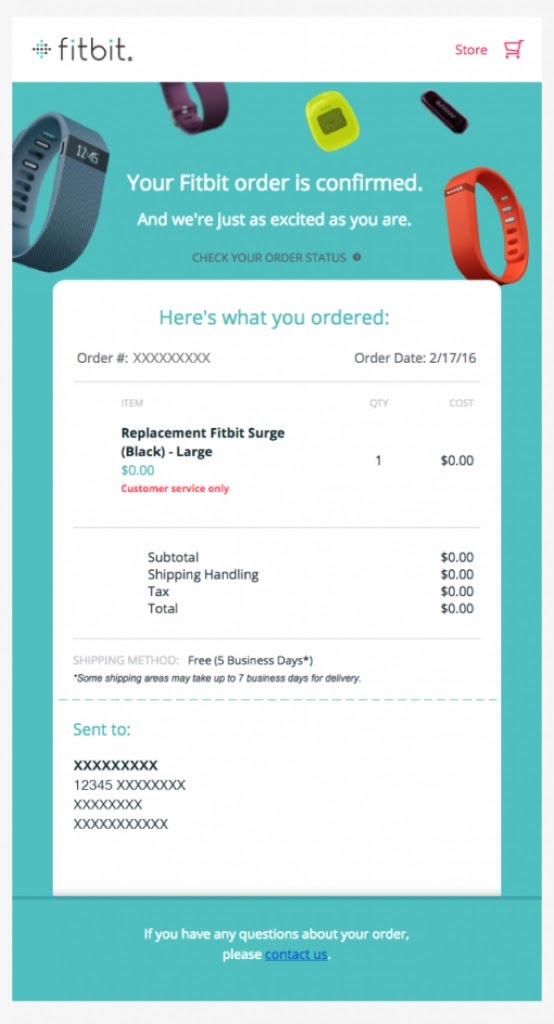
Following a subscriber’s purchase or registration for a conference, this transactional mail sends a confirmation email containing their shipment details and, if relevant, tracking links. Buyers often want to examine their order confirmation since it confirms that their purchase was completed and offers information on when their goods will be delivered. For example, Fitbit‘s purchase confirmation email contains a receipt and a link to track the progress of your transaction in real-time.
Depending on the sector, order confirmation emails have 80% and 90% open rates. As a result, they can be an excellent tool to cross-sell and up-sell your items. Indeed, according to Experian, transactional emails containing cross-selling products have a 20% greater transaction rate than those that do not—inside the email, requesting referrals. Additionally, you can use purchase confirmation emails to solicit recommendations from your subscribers. Specific merchants allow you to include an offer in the order confirmation email.
3. Email Notifications of Shipment
Another excellent transactional email example is a notification of delivery. Customers get shipping notifications after their order has been delivered, giving them peace of mind that it is on its way. By sending tracking details (or a link to monitor their purchase), consumers will know when to anticipate their order and plan to be home when it arrives.
Maintaining consumer awareness of the process’s progress may also assist in minimizing the number of emails and phone calls to your support staff.
At the same time, delivery confirmation emails, like purchase confirmation emails, may be used to promote your goods without being too aggressive. You may include similar things in your listing that the buyer might be interested in.
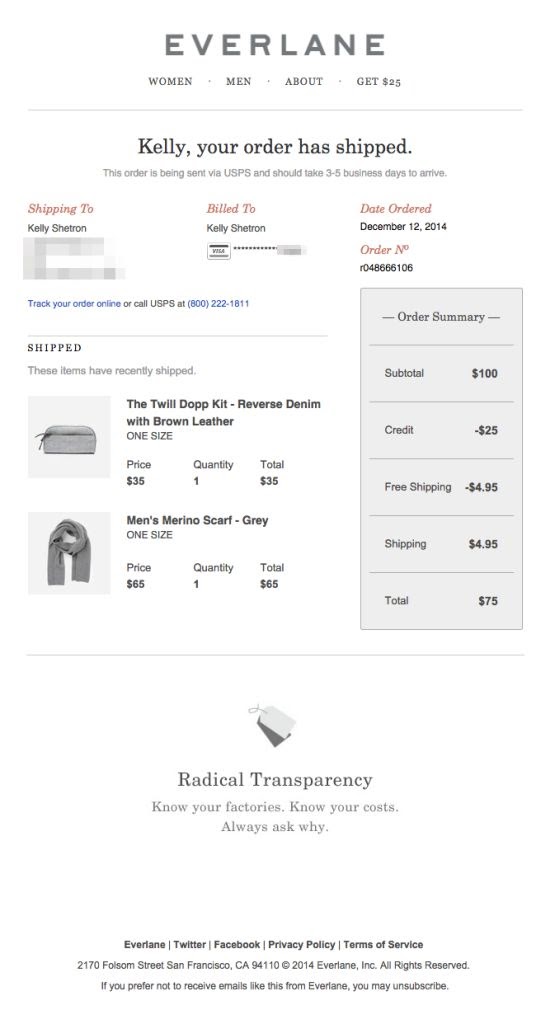
Look at Everlane‘s shipment notice email: Everlane’s order confirmation sounds welcoming and consistent with the brand’s tone of voice. The email also tells clients when they may anticipate the next update, showing that the delivery process is under control and relieving tension.
4. Emails Containing Password Reset Instructions
Users get the password recovery email in response to their request for a new password.
These emails provide information, guiding clients through the following stages to change their passwords. For that reason, reset emails must be sent promptly – when consumers reset their passwords, they expect to get their new ones immediately.
Emails, including password reset instructions, are critical for ensuring that consumers always have a connection to your product. Although the new password message is reasonably practical, the email does not have to be boring.
Consider the following examples of well-designed transactional emails from businesses that provide an exceptional client experience.
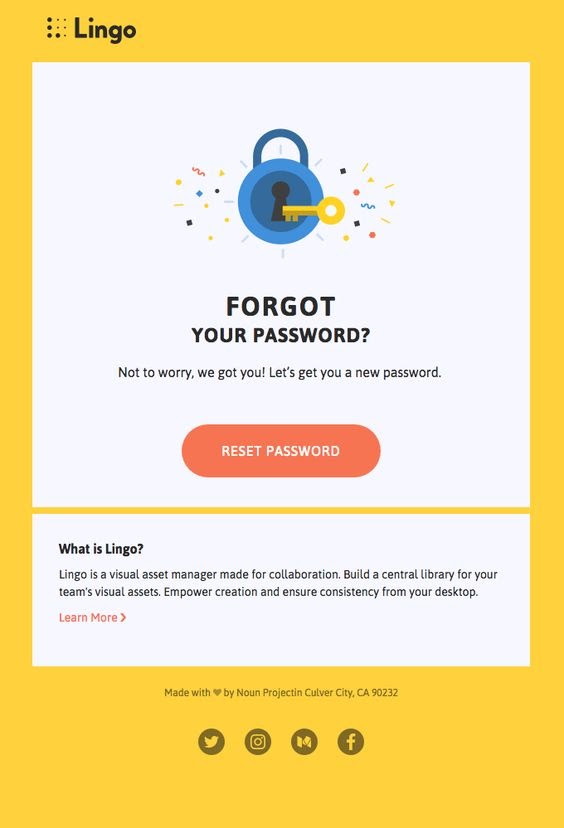
As you can see, the email is straightforward, but it links to its social media profiles. Although Password Reset emails are not intended to offer product recommendations, Lingo has made the most of its communication.
Notifying clients when a password recovery link will expire might be beneficial. If they do not immediately use it, they will instantly recognize the need to request another — avoiding unwanted emails to your support staff.
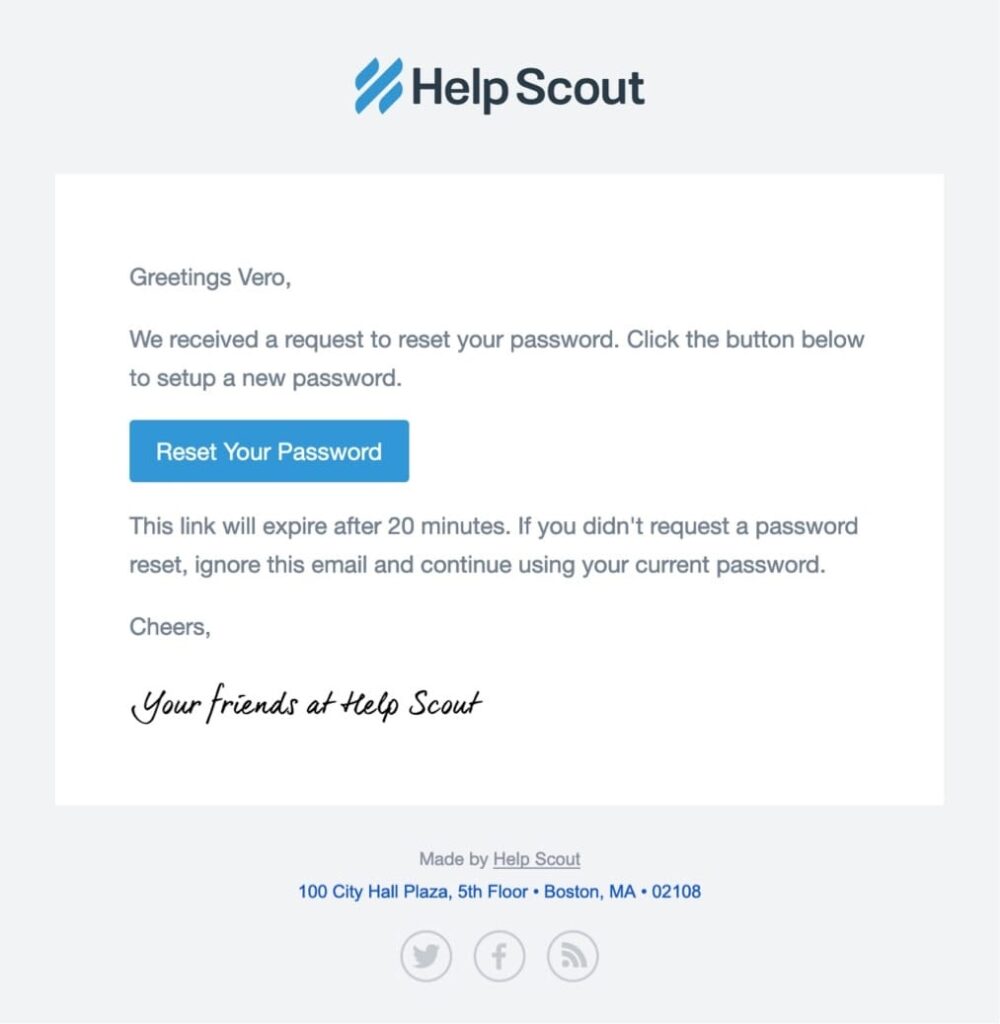
5. Email With Double Opt-in
When new subscribers sign up for your newsletter, you send them double-opt-in emails to ensure they want to get them (or other messages). By sending a double opt-in email, you can verify that the subscriber owns the email address, which may help reduce spam and enhance email deliverability.
For example, if someone joins your email list using a forged ID and you send them emails, you will harm your email domain reputation, and the email will never be read. Domain reputation is quite similar to the reputation we develop as individuals. It is influenced by your prior actions and the people you associate with.
In this case, you can send a simple message inquiring whether or not the subscriber wishes to receive your emails. In addition, businesses combine the Welcome Mail with a double opt-in email in many situations. Have a look at this transactional email example below.

6. The Email Notification of an Abandoned Cart
In 2019, the rate of global cart abandonment was 77.83%. It’s a significant obstacle for eCommerce websites.
However, for most businesses, a cart abandonment email can suffice. By and large, consumers open around 50% of cart abandonment emails, with 21% resulting in click-throughs. Around half of those who click make a purchase, according to Moosend.
So, the strategy is: Emails should be brief in their purpose. For instance, informing the consumer to “finish your purchase” or “check out now.”
Tips:
- Include a special offer to entice the buyer to return. If someone left for a cause, just telling them to return would not always be enough; thus, you must give them a reason to return.
- Maintain a timely manner. Generally, it’s better to send these emails within 30 minutes to a few hours, ensuring that you’re still striking while the iron is hot.
Emails sent in response to cart abandonment do not have to be dull. Instead, the email’s humorous content engages the viewer. Wich&Wire Co. provides a tremendous transactional email example for this situation. It sends notifications about goods that have been abandoned in the purchasing basket in a funny way that can attract customers.
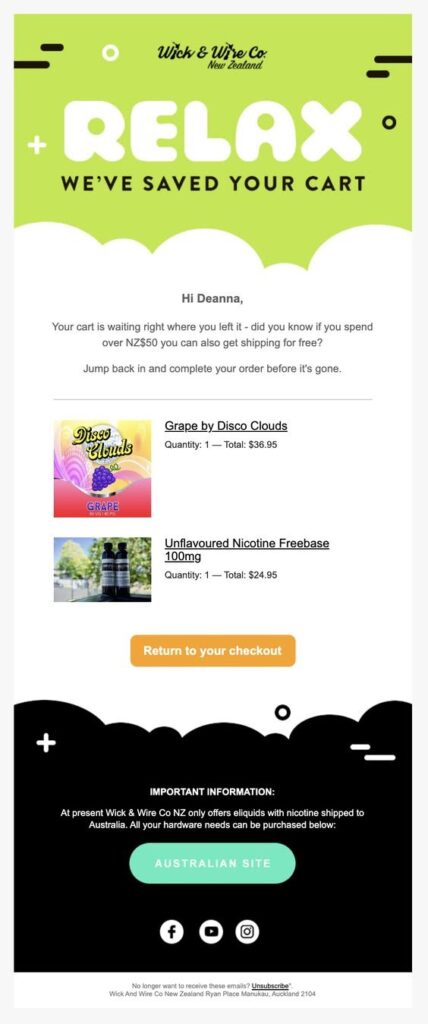
7. The Client Feedback Email
A customer feedback email is a practical approach to demonstrate to your subscribers that you value their input and present it publicly as a product review. These emails must be simple to read, with clear instructions and a prominent call-to-action (CTA) button.
Ascertain that you give appropriate context for the feedback you’re seeking – mainly if the consumer made the transaction some time ago.
Additionally, the following information should be included:
- For reference purposes, the time of purchase, the items bought, and the total purchase amount.
- Ascertain that the CTA button is visible and simple to click.
- Add no additional CTAs to divert the user’s attention away from the ultimate aim.
- Consider offering an incentive (such as a chance to win a $100 shop credit).
Artifact Uprising email perfectly exemplifies this situation: There is just one CTA button on the website, so there is no doubt about the email’s purpose. Moreover, it comes with a coupon for anybody who completes the survey.


Try FREE Email Builder demo today
Looking for a Magento 2 email editor that helps you create Magento transactional emails with no coding required?
Magento 2 Email Builder can help!
Best Practices for Transactional Emails You Should Follow
These are the best practices for using transactional emails that you should learn from.
1. Timing Is Critical

When sending a transactional email, getting the time right increases the likelihood of opening and reading.
Sending emails too soon may seem overbearing and unappreciated, while sending one too late may result in your consumers losing interest entirely.
Password reset emails, double opt-in emails, and purchase confirmation emails should be sent quickly. In addition, shipping and delivery information should be supplied immediately, and the standard norm for abandoned carts is 24 hours after abandonment.
2. Align Your Emails With Your Brand’s Tone of Voice and Visual Identity
Transactional emails that seem to have been slapped together fast can wreak an on your brand. Your emails should always reflect your company’s tone, appearance, and feel.
Transactional emails, like marketing emails, may boost your brand identity. Therefore, it would be best if you did not disregard them since they may contribute to the success of your marketing activities and provide a great consumer experience.
3. Ensure That the Subject Line Is Written Perfectly
Unlike marketing emails, transactional emails’ subject and preheader content should be brief and direct. Ascertain that the title tag is relevant to the addressee. Adding a little personality to a subject line is OK – as long as it does not detract from the email’s clarity.
It is critical to strike a balance while writing the subject line. Because when writing the title, you not only want to explain the email’s content clearly but also leave enough room in the email for the recipient to read it and locate what they’re searching for.
Return Path discovered that subject lines between 61 and 70 characters are optimal, whereas Campaign Monitor found that a tailored subject line increases open rates by 26 percent. Additionally, 56% of companies that used emojis in their subject lines had a better unique open rate than those that did not.
4. Personalize Your Transactional Email
Personalization entails designing something to meet an individual’s specific wants.
Personalized emails are more relevant than generic ones in a person’s inbox.
As a result, they generate more clicks. For instance, studies have shown personalized emails to increase transaction rates six times.
You can begin by personalizing the subject line using the recipient’s name. In addition, using dynamic content can personalize the message as well. Dynamic content has been pre-design, but specific data, such as name, may be filled in to make the email targeted to a particular individual.
5. Make Sure That It Is From a Real Person

Because real people manage your company, don’t make your emails look like they are composed and sent by a machine.
Avoid auto-generated, automated emails that lack individuality. Instead, ensure that answers are sent to a verified inbox that is examined regularly.
Sending emails from a no-reply email is the quickest method to convey to your consumers that you don’t want to hear from them. Furthermore, enabling consumers to answer reduces the likelihood of subsequent emails being marked as spam due to the higher interaction rate.
6. Separate Promotional Emails From Transactional Emails
Keeping your marketing vs. transactional email distinct is critical if you want to get into the inbox. Each email address will be paired with an IP address for sending emails. For different reasons, marketing emails may end up in the trash or spam folders, but order confirmation emails, for example, should not.
As a general guideline, promotional information should account for no more than 20% of the email’s content – but certain transactional emails may get away with this more than others.
Advertising information should not be included in customer feedback or password resets. However, shipment or purchase emails provide greater flexibility.
Additionally, the promotional information included in each email should be strategically positioned. For example, discount coupons and free shipping are probably not a brilliant idea in purchase confirmation emails – why offer free shipping when the consumer has already paid for delivery?
7. Mobile Optimization

Most emails are opened on mobile devices — 68 percent and 73 percent of consumers purchase across several media. As a result, your emails must be designed for mobile and desktop.
Most transactional email marketing software includes mobile-friendly templates – but if you’re developing your emails, test them properly.
Enhance the mobile-friendliness of your emails by:
- Maintaining concise topic lines
- Reducing the amount of body copy
- Using a single, unambiguous call to action
- Utilization of pre-header text
- Ascertaining that photos are not too tiny
- Enlarging text for mobile use if the text is too long
8. Increase Engagement by Including Social Media Connections
Transactional emails are not restricted to just verifying or recognizing business engagements. They can also serve as marketing by keeping your customers informed about things on your wishlist. In this scenario, I can’t help mentioning Nintendo. Nintendo‘s mailings include an enticing price reduction and significant social media buttons at the bottom.
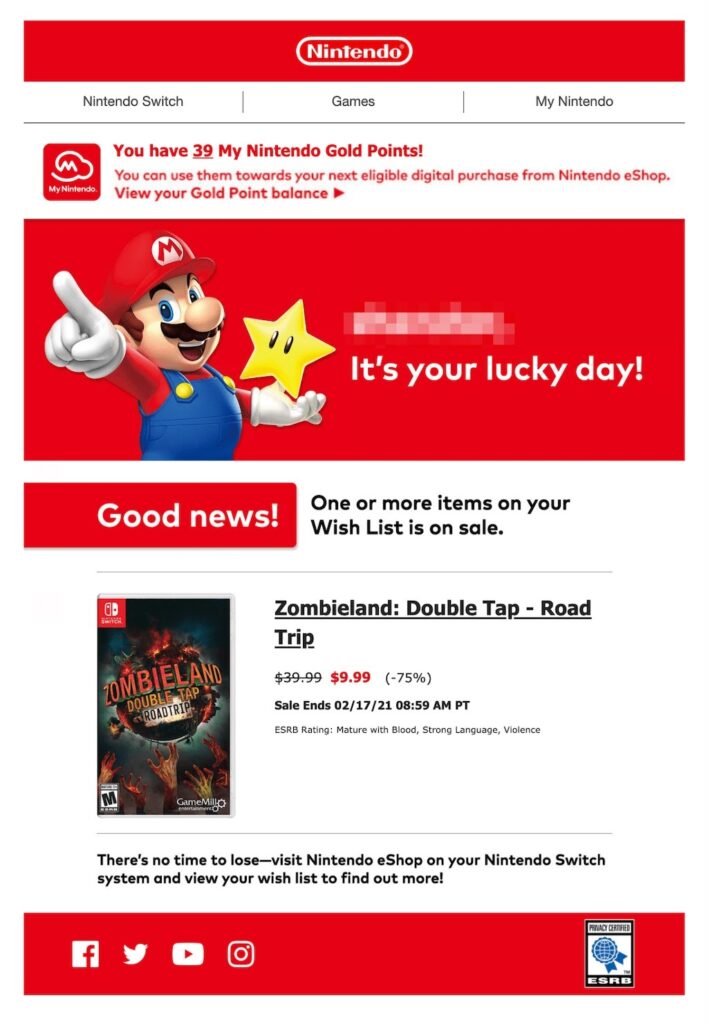
By including social network links in transactional emails, you can maintain consumer engagement after sending the email. While recipients are not interested in what you’re presenting at the moment, they can follow you on social media in the future to learn about new announcements or events.
Transactional Email Terms Explained
Expanding your vocabulary and familiarizing yourself with transactional mail language is essential in light of everything you’ve read. Finally, a quick glossary of essential terminology will round up this post.
1. API
First, let’s define the word API, which stands for Application Programming Interface. This is a software intermediary that enables the communication of two distinct programs.
An API improves the user and developer experience by automating and optimizing data transmission across apps. For instance, you may have real-time access to all your recipients’ data through your CRM.
2. API Tokens
API tokens, also known as access tokens, authenticate users when they send emails or access server-specific APIs. They are preferable to having a username and password because you may revoke or grant alternative access to an API token at any moment.
3. CAN-SPAM
The CAN-SPAM Act was enacted in 2003 to prohibit spam and provide a national standard for sending promotional emails in the US. The acronym stands for Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography And Marketing Act of 2003. The legislation establishes criteria for commercial message transmission, provides subscribers with the ability to unsubscribe, and imposes fines for noncompliance.
4. Blocklist

Occasionally, you may choose to exclude particular subscribers from your email list. For example, you may have come across catch-all domains when checking your email list using a program such as MailerCheck. Alternatively, you may need to restrict access to someone who requested their data be deleted following GDPR requirements. Under the Blocklist tab, such prohibited email addresses are displayed.
5. The IP Address Assigned Only to You (Dedicated IP Address)
A dedicated IP address is assigned only to your website. Unlike shared IP addresses, which are available to hundreds of websites, this form of IP address is dedicated to you. This is critical when sending emails since you are the only one responsible for the IP’s quality and reputation. The higher the rate, the more likely your email will be delivered. A separate IP address keeps possible fraudsters at bay.
6. APIs for Email
Email API is a more sophisticated kind of email sending. SMTP and POP3 are the two most used protocols for email delivery. They do this by enabling you to verify and exchange email messages between two individuals.
Today, email APIs provide all of the functionality of SMTP. In addition, it enables more efficient email transmission, enhanced personalization, and improved server-side feedback.
7. Domain

A domain is an address shown in the email header’s “From” field. To guarantee that transactional emails reach their intended recipients’ inboxes, you must first validate your domain’s DNS data.
8. Server SMTP Relay
Let us begin deciphering SMTP, which stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. This protocol is used to transmit outgoing emails (getting them from one email server to another).
There are also SMTP relay servers, which are third-party services that allow you to send bulk emails to mail servers. These servers are reputable third-party providers that can assist you with high-volume email sending and transactional email delivery. An SMTP server’s responsibility is to offer the technology and skills necessary to relay messages over SMTP.
9. Webhooks
Webhooks enable you to get real-time alerts about various events without repeatedly polling the API. It listens for events at your URL endpoint using HTTP callbacks to automatically trigger a response.
10. Suppressions
A suppressions list is a collection of rejected email addresses during delivery. The CAN-SPAM Act requires you to track subscribers who have unsubscribed or marked your email as spam. Additionally, the list contains bounces and any additional emails or sites you have blocked.
Wrapping Up
Transactional emails are undoubtedly vital as it assists you in establishing and nurturing connections with existing customers and prospects. It would be best to verify that you’re capitalizing on opportunities to boost traffic and income in all circumstances.
Above are the basics about transactional emails: the excellent transactional email examples, the difference between transactional vs. marketing email, when someone sends transactional emails, and the best practices for transactional emails you should follow.
Hopefully, this post has improved your understanding of transactional emails and the wide varieties you may use in your email strategy.

Try FREE Email Builder demo today
Looking for a Magento 2 email editor that helps you create Magento transactional emails with no coding required?
Magento 2 Email Builder can help!
Featured photo by Karolina Grabowska from Pexels.
 Magezon Blog Help Merchants Build Comprehensive eCommerce Websites
Magezon Blog Help Merchants Build Comprehensive eCommerce Websites